Templar Services
Effective Client CoNVERSATION
Meeting Preparation
Things to consider/remember
- Determine overall objective
- What three key selling messages will support the objective
- Support key selling messages with relevant content (data, examples, case studies, etc.)
- Use PPPC to create your opening / agenda with the client
- To close deliver a very brief reminder of the three key points and plan your pivot to the Call to Action or Q&A
- What the 5-6 toughest objections you’d least like to have to deal with?
- What is your ‘gold prize’ and ‘silver prize’ from the meeting?
High level meeting objectives
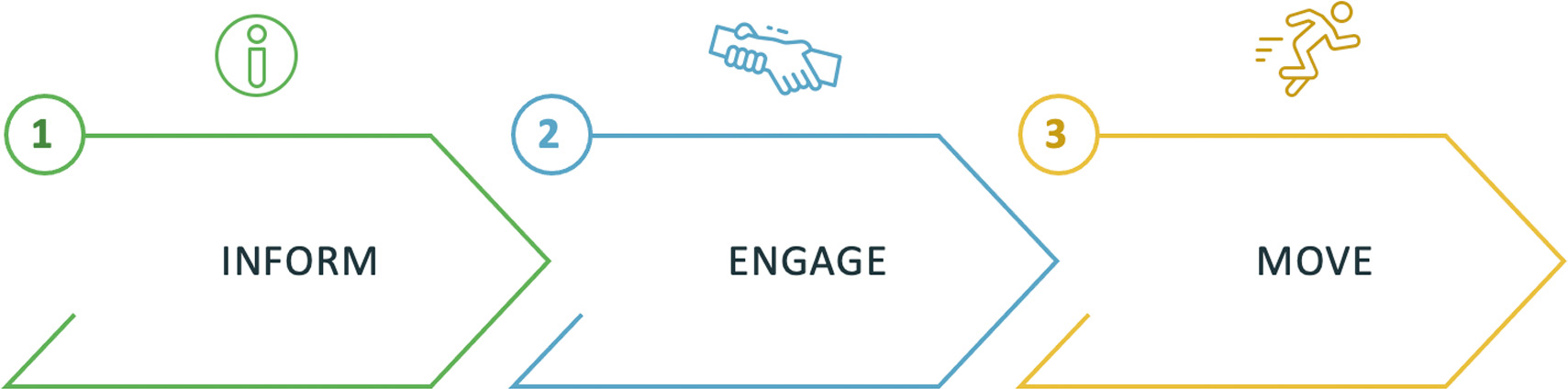
INFORM
- Communicate relevant, actionable ideas
- Tell them things they don't already know
- Don't lecture / push products
- Communicate insight and messages
- Benefit vs. risk/use fear factor
- Avoid 'shopping lists'
ENGAGE
- Build your personal franchise
- Generate trustworthiness and expertise
- Communicate as an authority
- Stimulate dialogue - don't 'present'
MOVE
- Be objectives-driven
- Flex the approach and your style
- Build the need throughout
- Problem-solve and collaborate
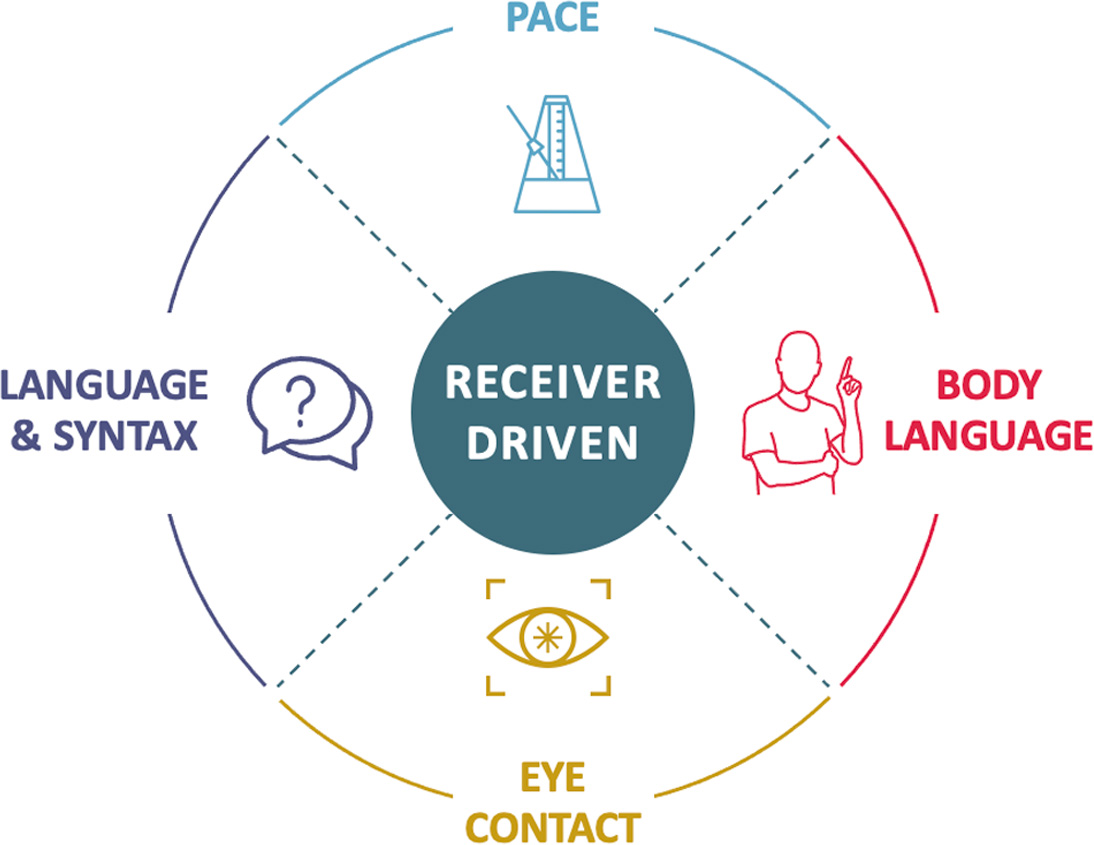
Initiate Dialogue
Your ‘conversational style’ is best adapted to meetings
- Pace: Pause frequently so listeners can process your ideas
- Eye Contact: Make eye contact and pause when making an important point or finishing a thought – “stick the landing”
- Body Language: Hands above the table and gesture as you normally would. Maintain good posture seated close to the table
- Language: Avoid jargon and long sentences. Be crisp, be precise
- Use questions to encourage dialog – avoid delivering a monologue
Start with impact: PPPC
- Purpose: What is the meeting about?
- Process: How will the meeting proceed? Agenda and logistics
- Payoff: Why does the client care? What is the benefit to them?
- Check: Get listeners ok to proceed


What are we here to achieve?
(Be clear on objective, mutual 'exam question')

How should the meeting run?
(Legitimise meeting agenda, time check, tone & feel)

Why should you engage in this interaction?
(Sell the benefit, be relevant, 'front-run' you key messages)

Validate and confirm objectives
(Get client buy-in, ask q., align on priorities)
Consult, Understand & Explore
The 4 C’s Strategic Questioning
- This line of questioning should be planned in advance based on what we know or suspect regarding the clients problems/challenges
- ‘Tell and sell’ versus ask. Ask the client questions to uncover the client’s hitherto unrecognized need
- Context: Broad open-ended question that determines the topic. Now listen intently for implied challenges/problems
- Challenge: Focus on the challenge/problem mentioned and have the client make it explicit
- Consequence: Ask questions that confirm that other problems flow from the one already identified, “how does that impact your…?”
- Conclusion: The solution is implied in this question, and it is designed to get the client asking for more about your solution, “What if we could provide you with a dashboard that….?”
- Client reply: “Yes, that would be of interest, how would it work?”

- Assess terrain, establish client's state of affairs
- What is the client's strategic and tactical environment?

- Makes implied issues explicit for the client
- What difficulties does the client

- Clarify effects & implications
- What are the outcomes of either resolution / irresolution of challenges?

- Solution, pre-empt objections
- What does the client see as the benefits of the solution you propose?
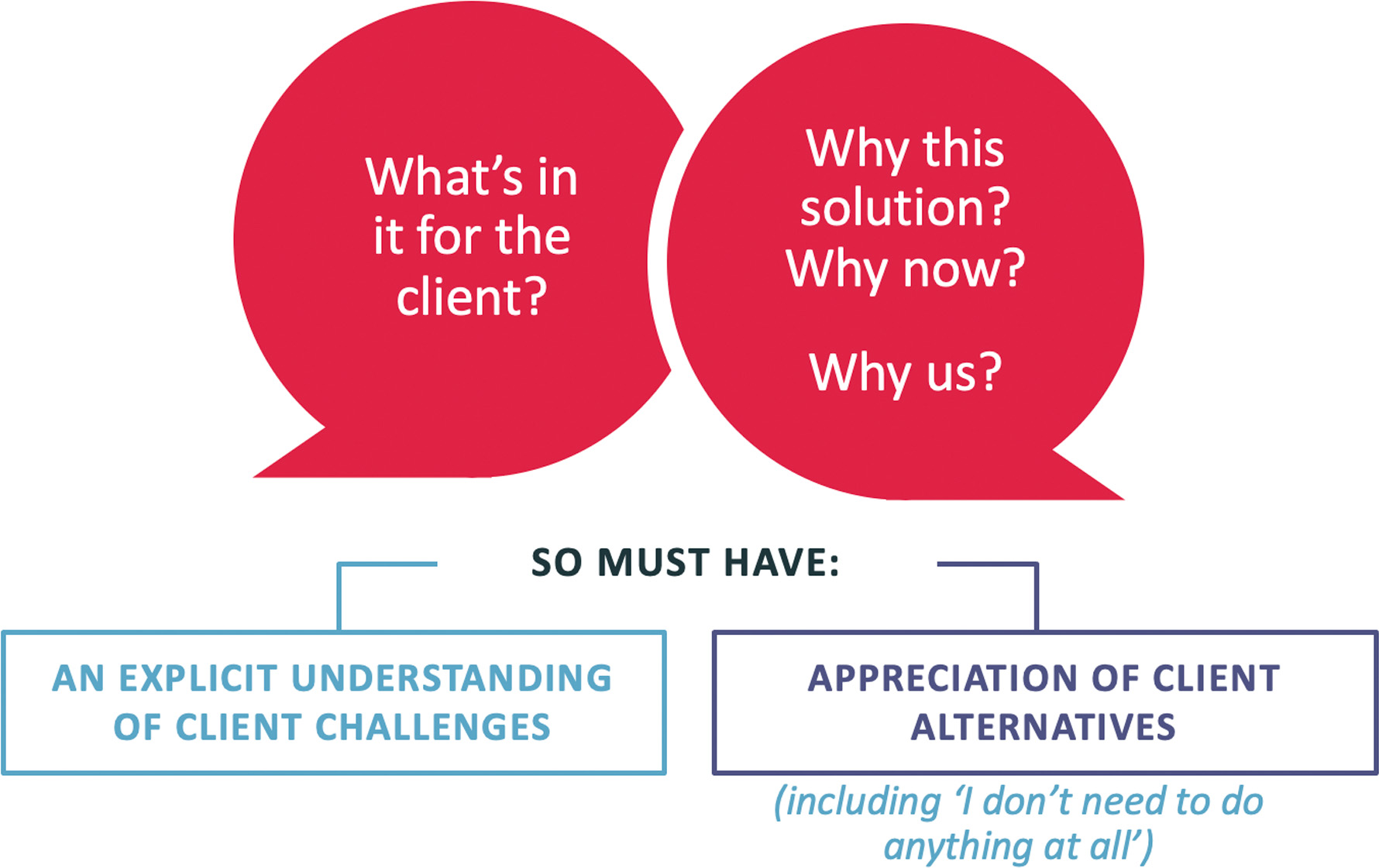
Analyse and Match Client Needs
Features, Advantages and Benefits
- Assume the client is thinking: “So What?!” and “What’s in it for me?!”
- Features and Advantages cannot answer the WiiFM question – only explicit benefits to the client can
- Whenever we talk about features and advantages (products and services) we have to attach an explicit benefit – why do they care?
Communicate & Validate Solution
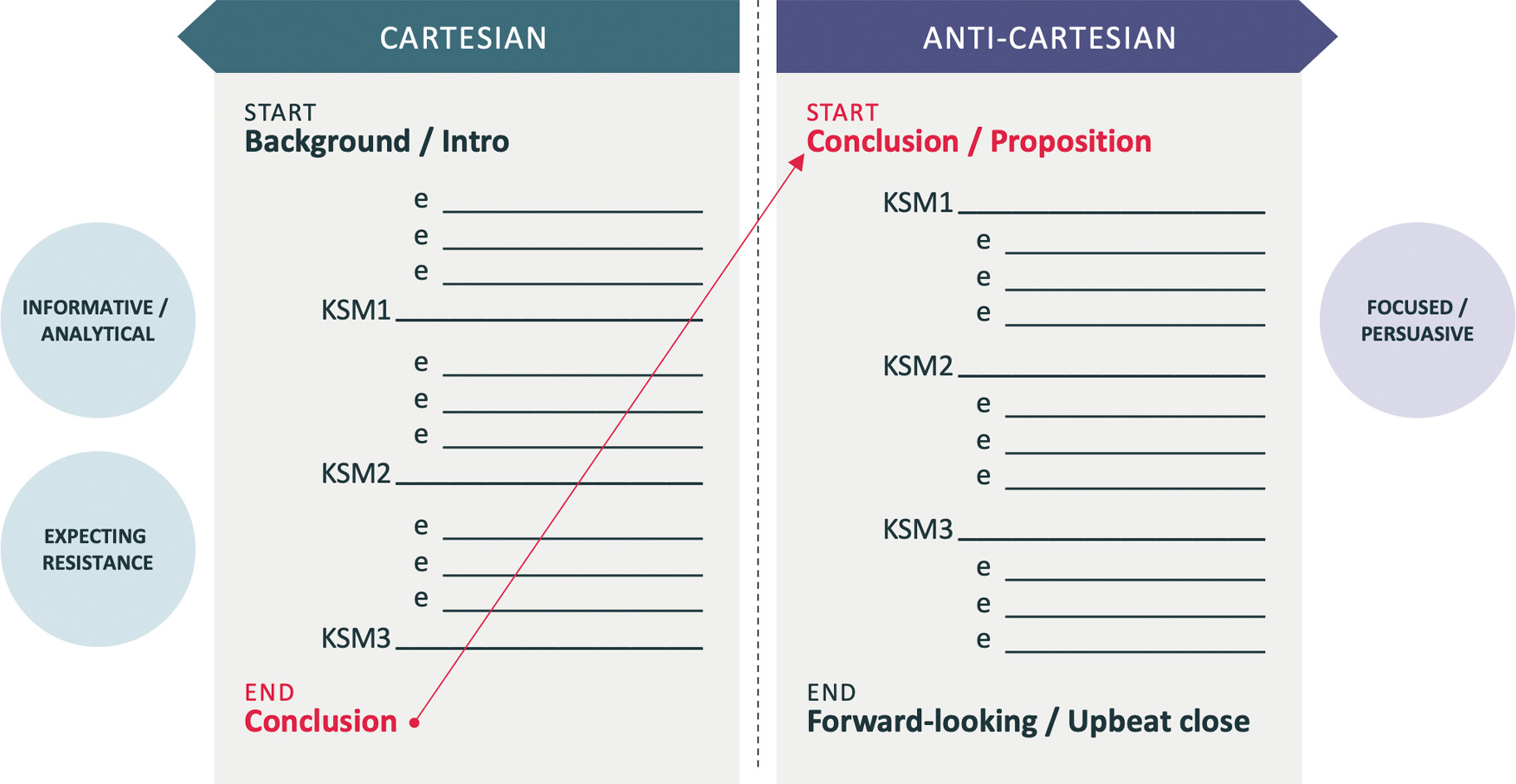
Message Structure: Cartesian v Anti Cartesian
- Lead with your key selling message and then validate with the facts and data
- Don’t just deliver a laundry list of facts
- Assertions made without proof can be dismissed without proof
- Don’t show all your homework, present the three most powerful and compelling key selling points
- The three key points should all support the conclusion
- Stop in between key points to encourage dialogue – i.e “where would you like to go deeper?”
Fear Factor
- Tapping into the fear of loss is more powerful than tapping into the desire for gain. Sell fear when the client is in a state of inertia
- Sometimes present the benefit as the bad thing not happening rather than the good thing happening
INTERIM COMMUNICATION
Navigate Challenging Dialogue
Validation of Concerns
Handling objections
Your job is to surface all of the stated and unstated concerns the client might have. Residual unstated objections makes it almost impossible to close.
Techniques to answer the objection:
- Pre-empt: raise the objection before they do
- Ask for more: get more information
- Isolate: put the objection to the side temporarily and confirm the value of the offering/solution
- Boomerang: Turn the objection into an advantage
- Agree, counter: Avoid “but” or “however”
- Straight denial: only when necessary
- Take a thinking pause
- Acknowledge by repeating or rephrasing the objection
- Validate the objection by confirming it is legitimate
Handling objections
Your job is to surface all of the stated and unstated concerns the client might have. Residual unstated objections makes it almost impossible to close.
Techniques to answer the objection:
- Pre-empt: raise the objection before they do
- Ask for more: get more information
- Isolate: put the objection to the side temporarily and confirm the value of the offering/solution
- Boomerang: Turn the objection into an advantage
- Agree, counter: Avoid “but” or “however”
- Straight denial: only when necessary
- Take a thinking pause
- Acknowledge by repeating or rephrasing the objection
- Validate the objection by confirming it is legitimate
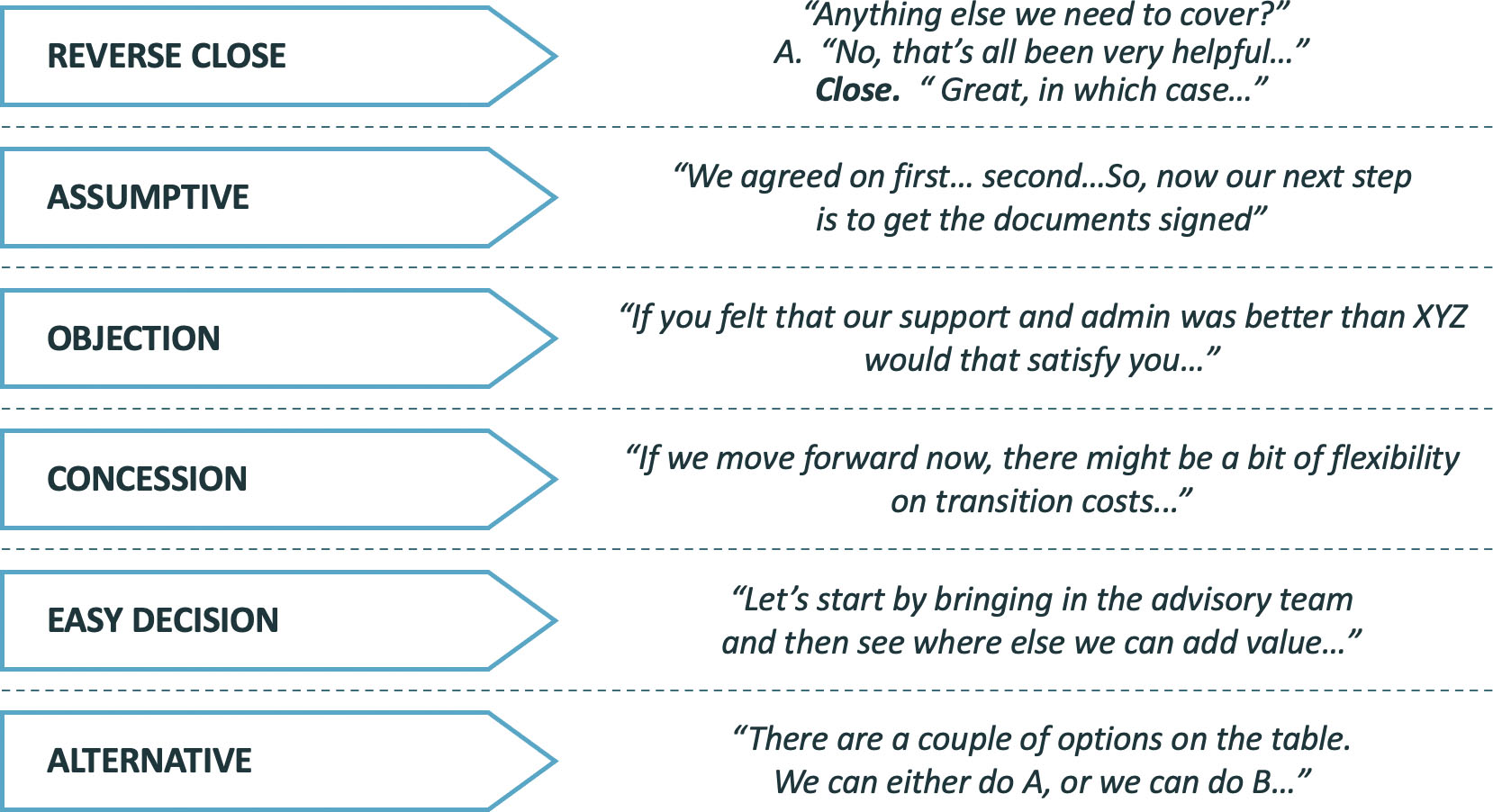
Agreement & Close
Buying signals’, closing and follow-up
- Follow-up: Don’t volunteer to do things, ask whether it would be helpful
- Make sure the client is ‘on the hook’ for follow-up
- Objections often have a hidden ‘buying signal’ buried in them: Sell to the buying signal then ask the follow-up question
Getting to Agreement
REVIEW MEETING
Feedback, celebrate & migrate successes, learn from setbacks
RECOMMENDED READING
Books
Communications – General
Human Communication
By Joseph A. Devito
Chapter 4: Listening in Human Communications
Chapter 18: The Persuasive Speech
Dialogue and the Art of Thinking Together
By William Isaacs
Part III: Predictive Intuition
Selling & Pitching
By Nicholas Read and Stephen Bistritz
Chapter 4: How to Gain Access to the Executive Level
By Neil Rackham
Chapter 4: The SPIN Strategy
By Brian Tracy
Chapter 10: Closing the Sale
Relationship Building and Negotiation Skills
By Robert Cialdini
Negotiation Skills for Managers
By Steven Cohen
Research
Neuroleadership Journal. Issue One. 2008
SCARF: A Brain Based Model for Collaborating With & Influencing Others
Business Review Articles
Harvard Magazine
The Psyche on Automatic: Amy Cuddy on how to become an ‘Alpha Dog’
Harvard Business Review
How to Buy / Sell Professional Services (66213 – PDF – ENG)
The New Science of Building Great Teams (R1204C)